HSA is a health savings account. Don’t get fooled by the name. It can go, beyond health savings. Not many know, that HSA is the best tax-advantaged account in the USA. Even better than a 401K. How is it better? We will take a closer look at it in this episode.
HSA Contribution
You can contribute to HSA, only if you meet two conditions. The first condition is, just like a 401K, HSA has to be offered by your employer. The second condition is, you should be on an HDHP, High Deductible Health Plan. If you choose to have a PPO plan, then you will not be able to contribute to HSA. A high Deductible health plan, is a requirement for you to contribute to HSA.
How much can you contribute? For 2023, you can contribute up to, $3,850 just for yourself. But if you have your whole family under your coverage, then you can contribute up to, $7,750. So the maximum a family can contribute to their HSA is, $7750 per year.
Many assume, that the money contributed to HSA, needs to be used within that specific year. But it is not true. It is true only for, FSA. Not for HSA. For HSA, unused money gets rolled over into the next year. For example, if you contribute $7000 this year, and if you used only $2000 for your healthcare expenses, then the remaining $5000 will be, rolled over into next year. Just like your savings account. It is called a Health Savings account for a reason, right?
Though it is like a savings account, it does have a neat, twist to it. You have the option of, investing your savings in mutual funds, just like in a 401K. But every plan has a certain minimum amount, that you need to maintain in your cash account, before you can invest in a mutual fund. Mostly it is $1000. So you can set up your account in a way, so that any new contribution that goes over your cash limit, gets automatically invested in a mutual fund.
“But Vijay, I can do all these in a brokerage account. What is so special about HSA?” Tax advantage. Not just one. Triple tax advantage. You do not have to pay tax on the contributed money, No tax for any gains from the investments, and as long as it is used for a qualified medical expense, No tax for withdrawal as well. So there are 3 tax advantages for an HSA. No other plan in the US, has this unique triple tax advantage.
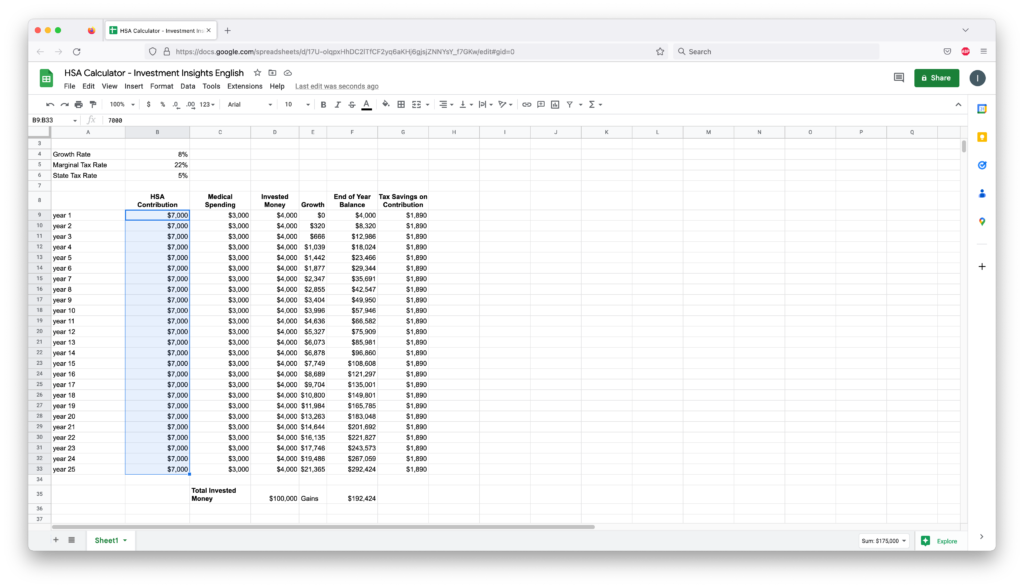
For example, let’s say that you contribute $7,000 every year to your HSA. But you use only, $3000 every year for your medical expenses. And so the rest of the contribution $4000, is invested and it is growing at a rate of, say 8%. If you are in the 22% marginal tax bracket, and if your state tax is 5%, then you will be saving, $1890 per year on taxes. This is the first tax advantage.
Let’s say that you continue to do this, until your retirement in 25 years. By the end of the 25th year, you will have an HSA balance of, $292,000. Of which, $100,000 is your total contributed money, and $192,000 is capital gains. Now, there is no tax for this gain of, $192,000 as well. This is, the second tax advantage.
Both the first and the second tax advantage, 401K has them as well. No tax for contributions, and no tax for capital gains. But where HSA gets better than 401K is, the third tax advantage. If used for qualified medical expenses, then there is no tax for HSA withdrawal. But in a 401K, when you withdraw the money after retirement, the withdrawal amount will be considered as your income for that year, and you will pay tax for that income. This is why, an HSA is better than a 401K.
Non-Medical Expenses
But what if you withdraw from an HSA, for non-medical expenses? Then those withdrawals will be considered ordinary income, and you have to pay tax on those withdrawals. Just like in a 401K. So essentially, at best, HSA has a triple tax advantage, better than a 401K. At worst, it is like a regular 401K.
This is assuming that you are withdrawing after your retirement age of 65. But if you withdraw for non-qualified expenses, before you turn 65, then you have to pay the tax, and also a penalty of 20%. So it is not a good idea to withdraw from HSA, before retirement for non-qualified expenses. Qualified medical expenses can be withdrawn at any time, with no tax or penalty.
Leaving the company?
But what if you leave the company? If you leave the company, you have 2 options. Leave the HSA account as it is with your old employer. But the problem is, you have another additional account to manage. Also, there will be extra fees for the account maintenance. A better option is, to move the HSA balance into your own HSA account. Yes, you can open your own HSA account. Just that you cannot contribute directly to it. But you can roll over your HSA balance, from an existing HSA account. Fidelity has a good HSA plan with no fees.
Now let’s look at the qualified medical expenses. You can use your HSA, to pay for your deductible, coinsurance, and copay. For example, you have a health insurance plan, with $3000 deductible, 20% coinsurance, and a $50 copayment. For every doctor visit, you will be paying, $50 copayment. This can be paid thru your HSA. And you will be paying 100% of your healthcare expenses, until you reach your deductible limit of, $3000. That whole $3000 can be paid using HSA. After you meet your deductible limit, you have to pay, 20% of all the healthcare expenses – because you have a coinsurance of, 20%. That can be paid using HSA as well. In short, for any medical expenses that you are paying from your own pocket, you should be able to pay with your HSA. Even if you are in, another country.
How about health insurance premiums? Yes, we can pay certain healthcare premiums, but not all. By default, HSA cannot be used for health insurance premiums. But there are a few exceptions to that rule. If you lose your job, and if you decide to continue your employer’s healthcare under COBRA, then you can use HSA, to pay for the COBRA plan premium. Another exception is, if you are getting unemployment compensation, then paying a healthcare premium during that period, can be covered by HSA. These 2 exceptions are applicable during your working years.
But after 65, you can use HSA to pay, certain medicare insurance premiums. There are 4 different medicare insurance – Part A, for inpatient hospitals, Part B for Doctor visits, Part C – a combination of Part A and Part B, with some additional benefits, and then Part D, for prescription drugs. Among these, Part B and Part D premiums, can be paid thru HSA. Other than the medicare premiums, long-term care premiums can be paid using HSA as well, though it has limits depending on your age.
You can check the HSA bank site, to see the list of qualified medical expenses for HSA.
Knowing these characteristics of HSA, are there any ways to maximize these HSA benefits? Yes, there are. There are a few strategies that people follow. They max out their HSA contribution every year – contributing $7750 to their HSA. Let’s say that their insurance plan, requires an out-of-pocket maximum of, $8000. That means, the maximum they have to pay for healthcare expenses in a year is, $8000. Most of them, do not spend all the contribution. And so, by the end of the year, they have a size-able balance in their HSA. They start building their HSA balance, until it reaches $8000. Let’s say that it happens in 2 years. Starting from 3rd year, they will always keep this $8000, in their HSA cash account for emergency needs, and start investing the additional contribution, in equity mutual funds. This will help them, to build a nice balance in their HSA, by the age of 65.
There are certain folks, who take this strategy to the extreme. Knowing that healthcare expenses will be a lot more expensive after 65, they will not pay any healthcare expenses with their HSA now. They will just contribute to their HSA, and start building the HSA balance. Though they do not use HSA to pay healthcare bills, they save all their healthcare receipts. Because, those receipts can be used to withdraw HSA funds, anytime in the future. The idea here is, to give maximum time, to all the HSA contribution money to grow. By not withdrawing now, the balance grows tax-free for future healthcare expenses.
After retirement, a married couple would spend, close to $300,000 on average, for their healthcare. Now you can see, why certain folks are, building up their HSA balance for the future.
I hope this episode helped you to understand HSA better. Please share it with your friends and family, who can get benefit from this. Especially younger folks, who have just started earning. See you all soon in another episode. Thank you.

